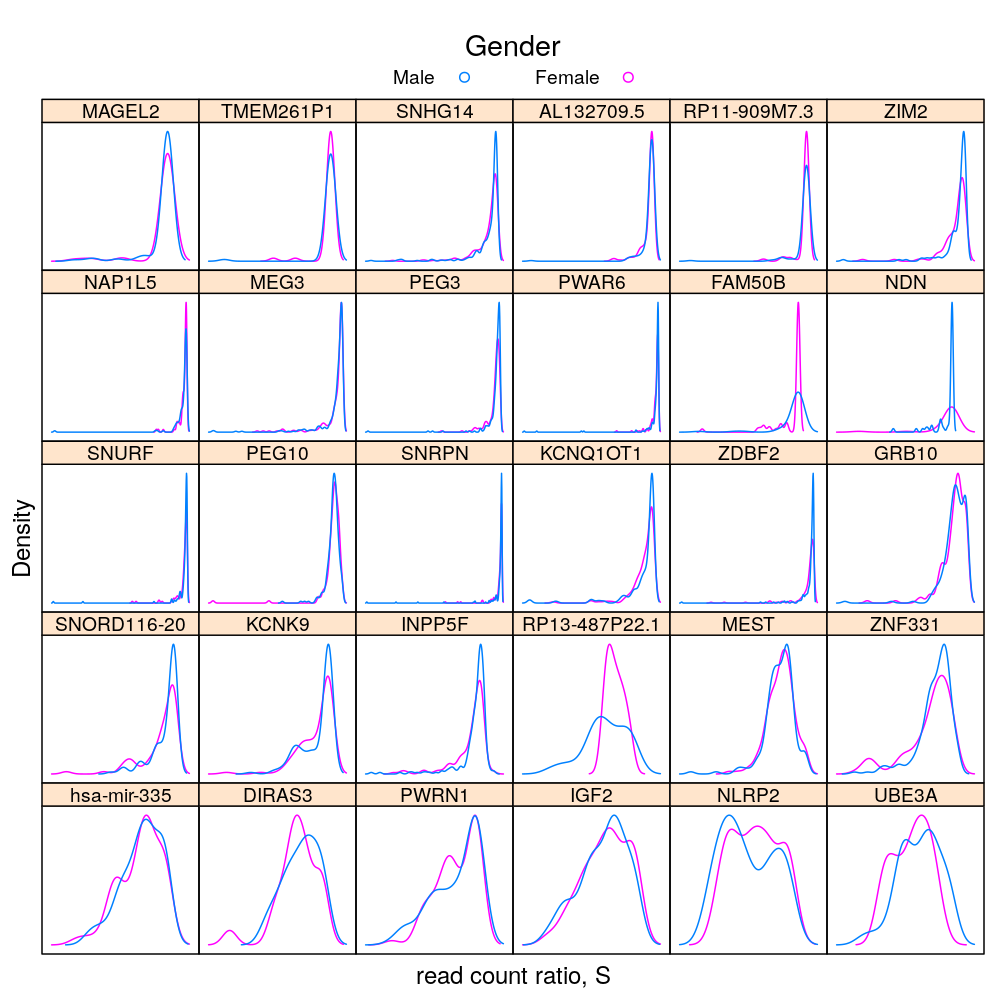
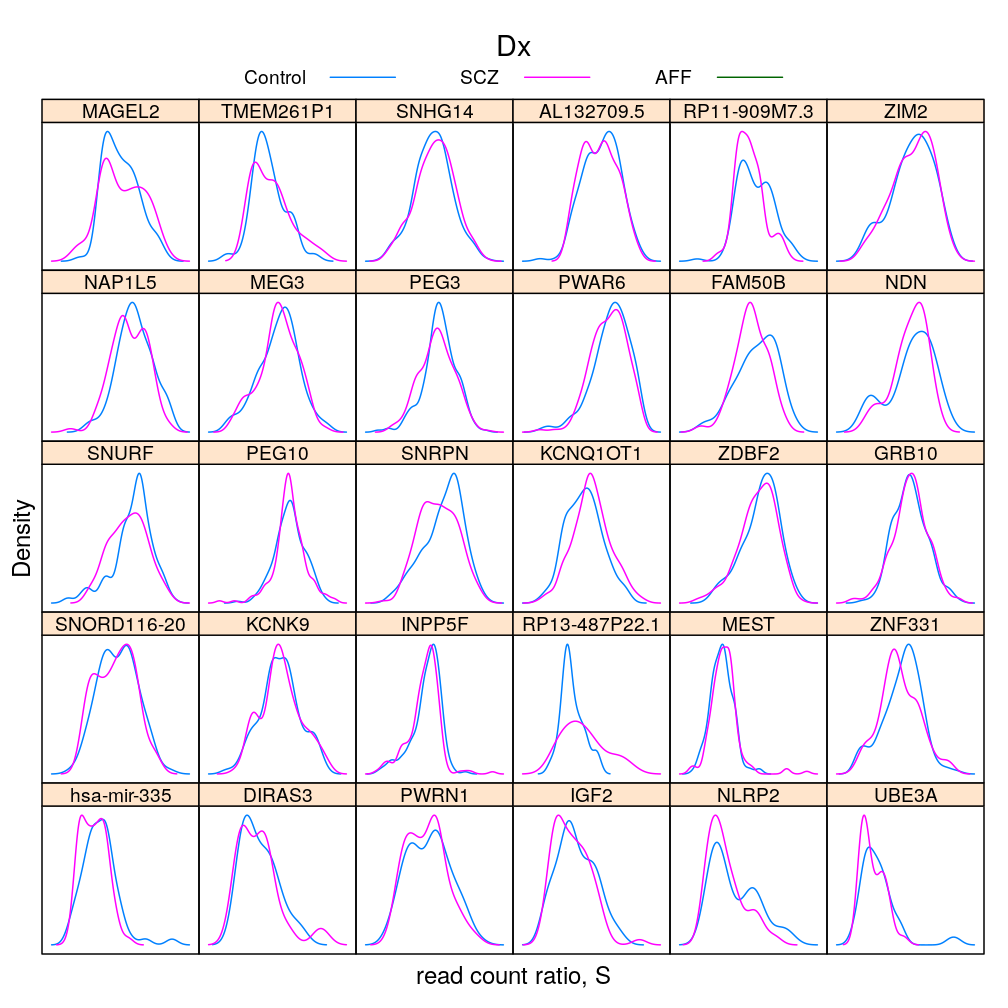
This analysis presents plots of the conditional distribution of the read count ratio statistic S or its quasi-log transformed version Q given each a gene a predictor of interest, which is either Gender or Dx. For the predictor Age see the previous post trellis display of data. In the present post a more detailed conditioning is done, using RIN and Institution for MEG3 and MEST. These are genes found in a previous analysis (see permutation test) to be significantly associated to Gender and Dx, respectively. The plots below show that the distributions greatly overlap between differing levels of gender or disease even for the most significantly associated genes, and that this holds in case of further conditioning on RIN and Institution.
A distinct but related question is also addressed here, namely the correlation between S (or Q) given one gene and that given another gene when the genes are near each other (in the same imprinted gene cluster) or far away (e.g. on a different chromosome). However, no clear pattern emerges from this part of the analysis.
Conditioning on a gene and some predictor(s)
Import data on read counts and predictors and cast them in convenient long format.
gene.ids <- unlist(read.csv("../../data/genes.regression.new", as.is = TRUE))
names(gene.ids) <- gene.ids
Y.long <- reshape.Y2long(gene.ids)
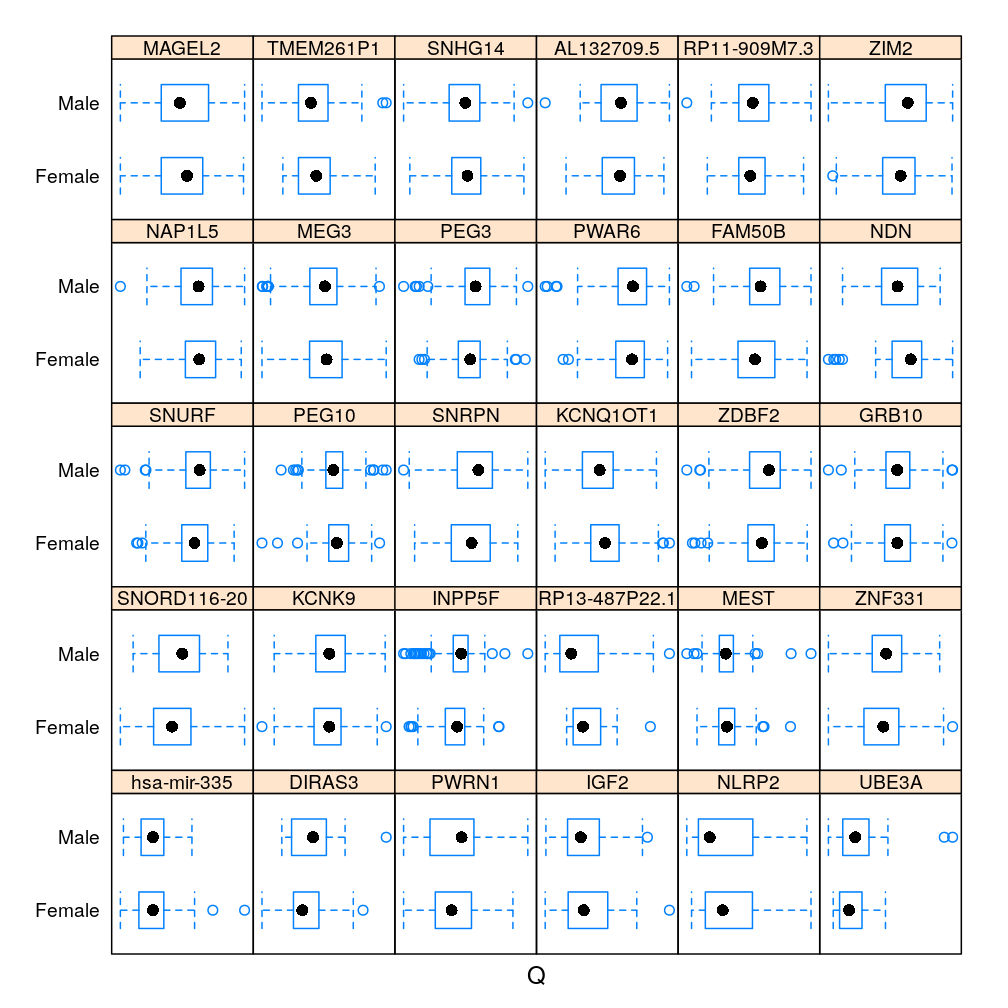
Gene and Gender
my.update <- function(dp, ...) {
update(dp, scales = list(x = list(draw = FALSE, relation = "free")),
par.settings = list(add.text = list(cex = 0.8)),
xlab = "read count ratio, S",
...)
}
S statistic
dp <- densityplot(~ S | Gene, groups = Gender, data = Y.long, plot.points = FALSE)[1:30]
update(my.update(dp, auto.key = list(title = "Gender", text = c("Male", "Female"), columns = 2, points = TRUE, lines = FALSE)),
par.settings = list(superpose.line = list(fill = trellis.par.get("superpose.symbol")$fill[c(2, 1)],
col = trellis.par.get("superpose.symbol")$col[c(2, 1)])),
scales = list(draw = FALSE, relation = "free"))
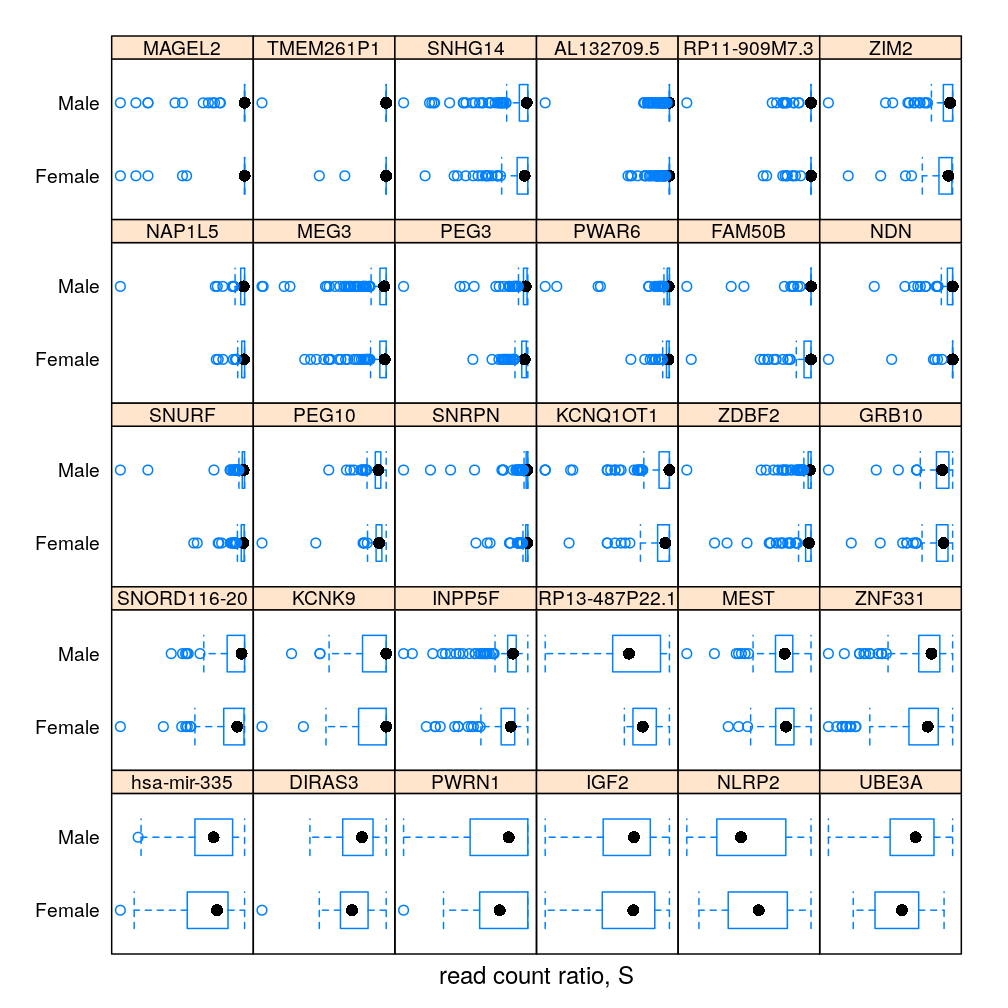
The same information in box and whisker representation:
dp <- bwplot(Gender ~ S | Gene, data = Y.long)[1:30]
my.update(dp)
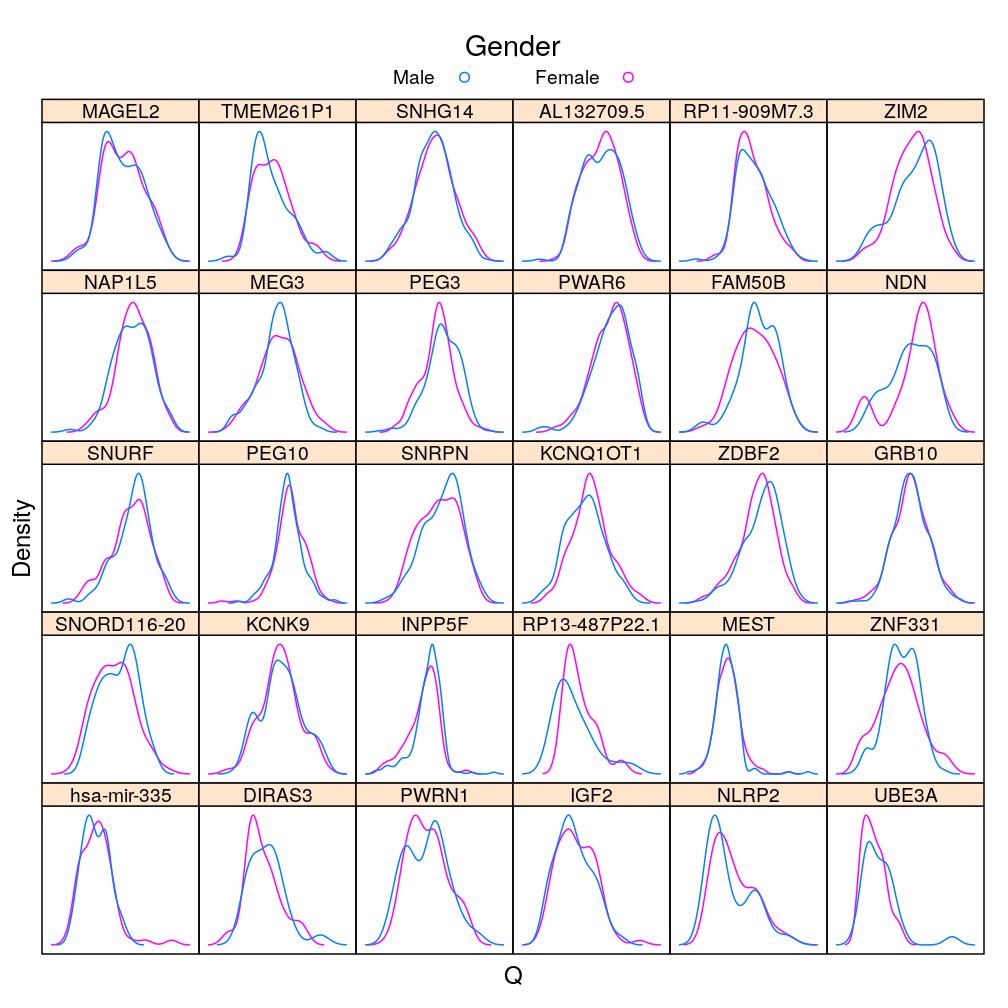
Q statistic
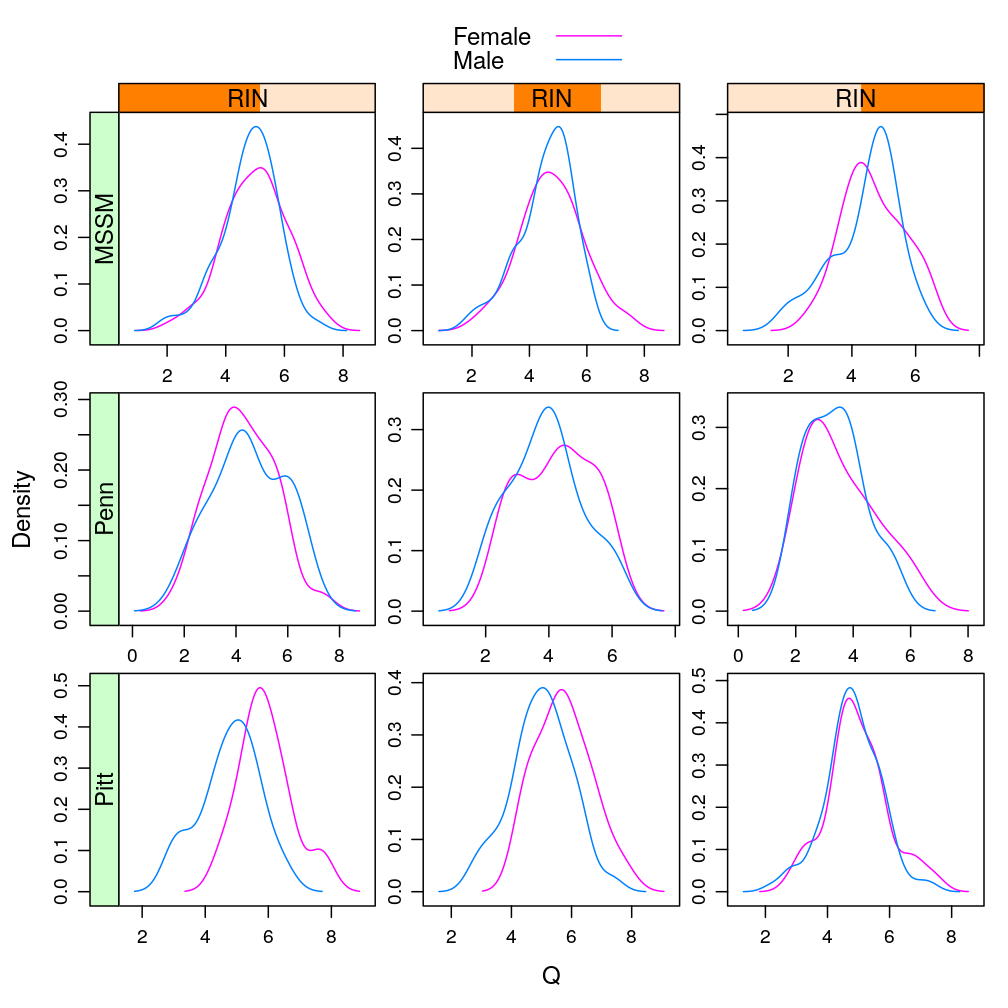
Only with MEG3, the most significantly affected gene by Gender (see a later post), conditioning on various RIN intervals
Y.long$RIN.copy <- Y.long$RIN
Y.long$RIN <- equal.count(Y.long$RIN, number = 3)
lp <- densityplot(~ Q | RIN * Institution, data = Y.long, groups = Gender, subset = Gene == "MEG3",
scales = list(relation = "free"), plot.points = FALSE,
par.settings = list(superpose.line = list(fill = trellis.par.get("superpose.symbol")$fill[c(2, 1)], col = trellis.par.get("superpose.symbol")$col[c(2, 1)])),
auto.key=TRUE)
useOuterStrips(lp)
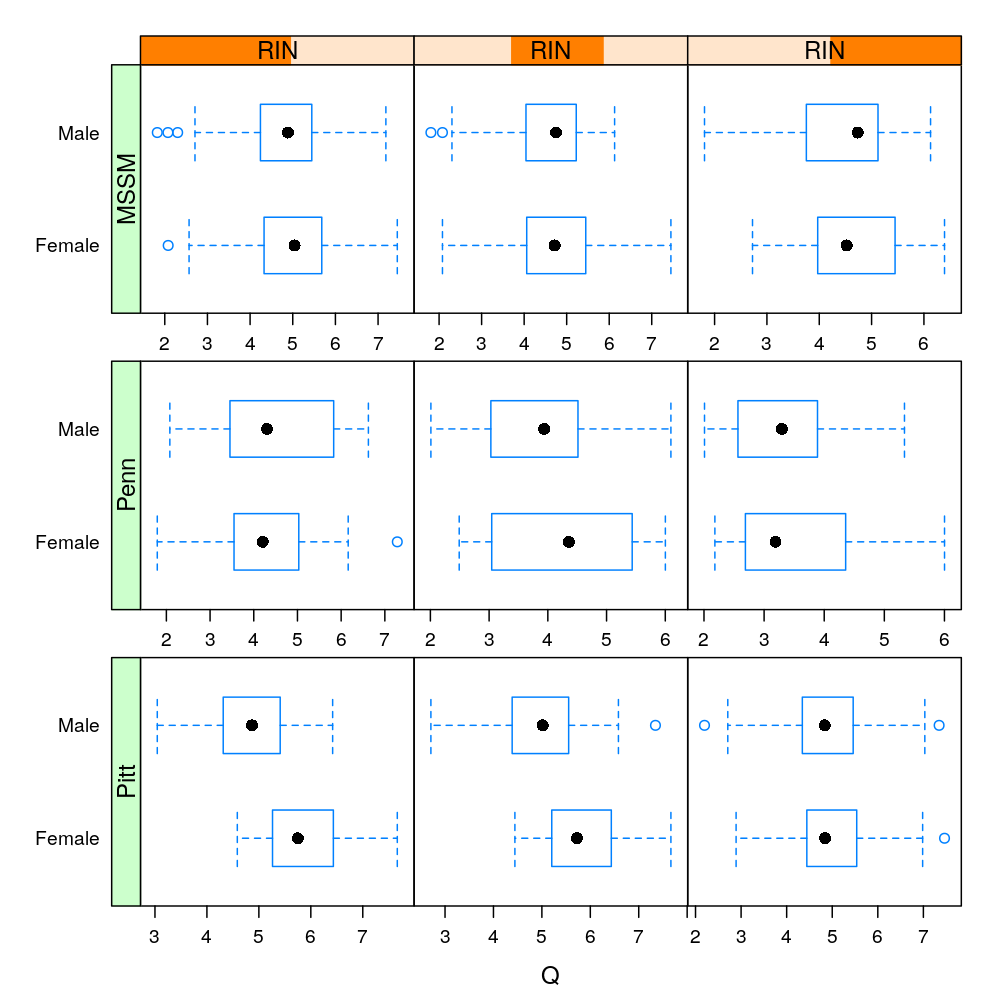
lp <- bwplot(Gender ~ Q | RIN * Institution, data = Y.long, subset = Gene == "MEG3", scales = list(x = list(relation = "free")),
auto.key=TRUE)
useOuterStrips(lp)
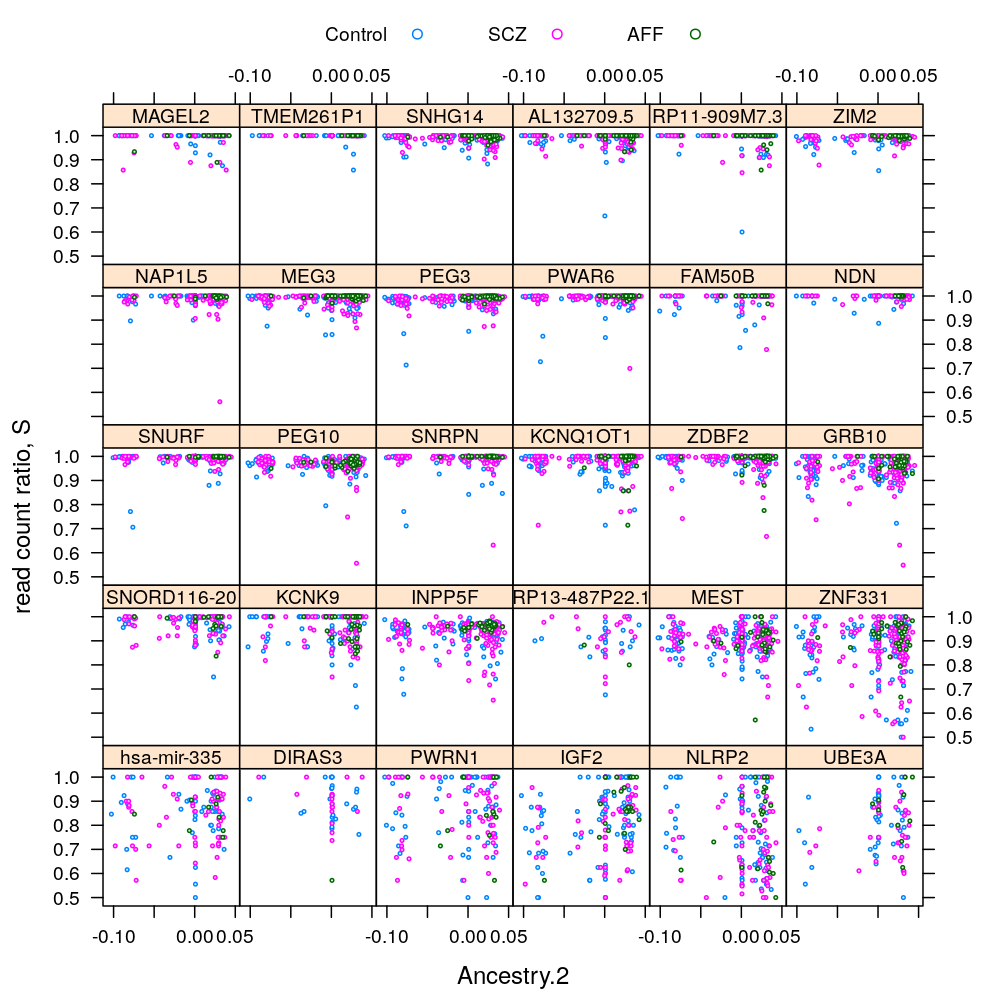
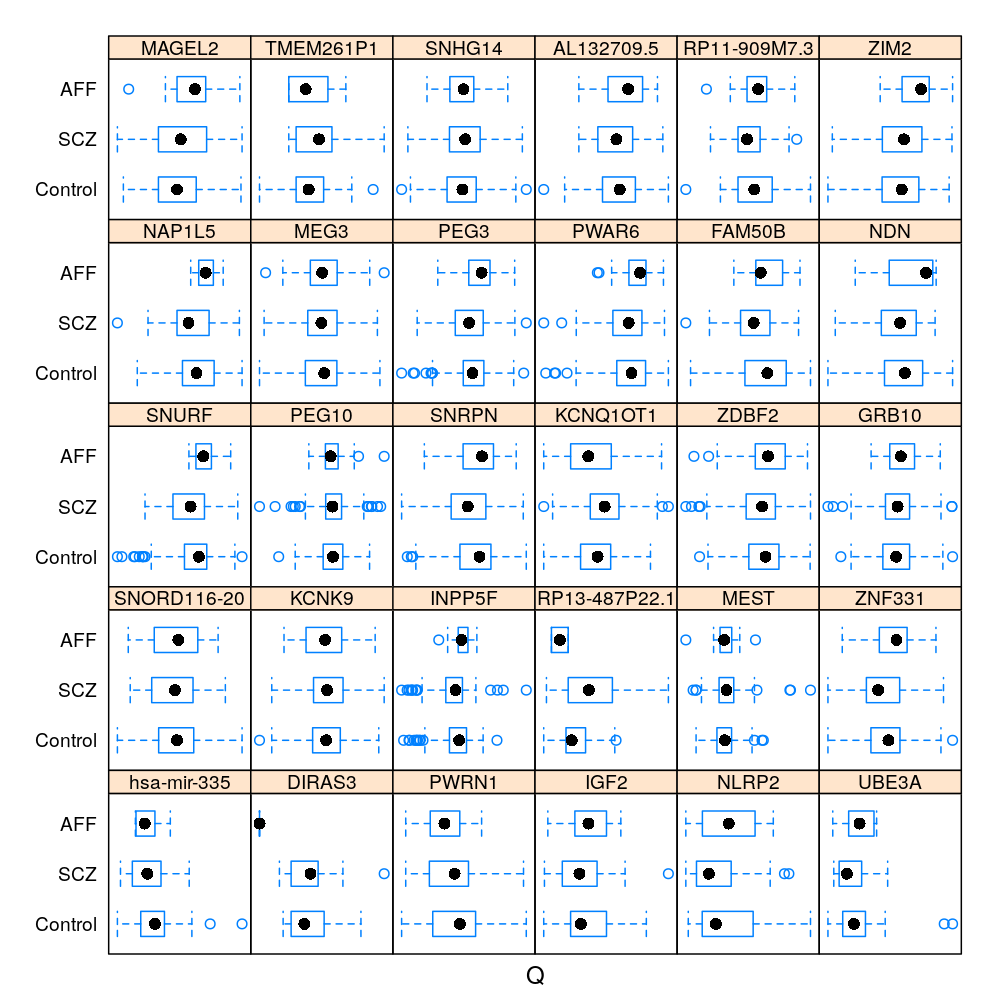
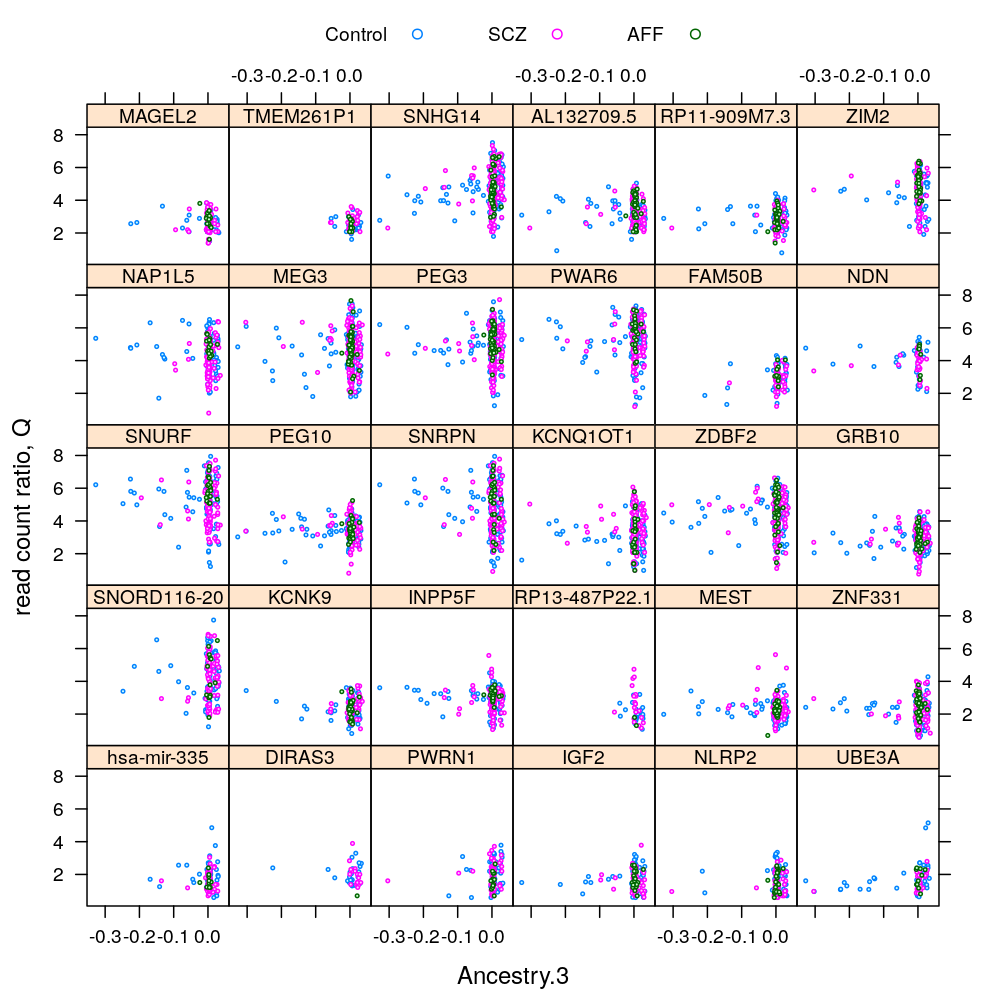
Gene and Dx
S statistic
For the density plots AFF had to be excluded (for some genes there are too few AFF individuals for kernel density estimation)
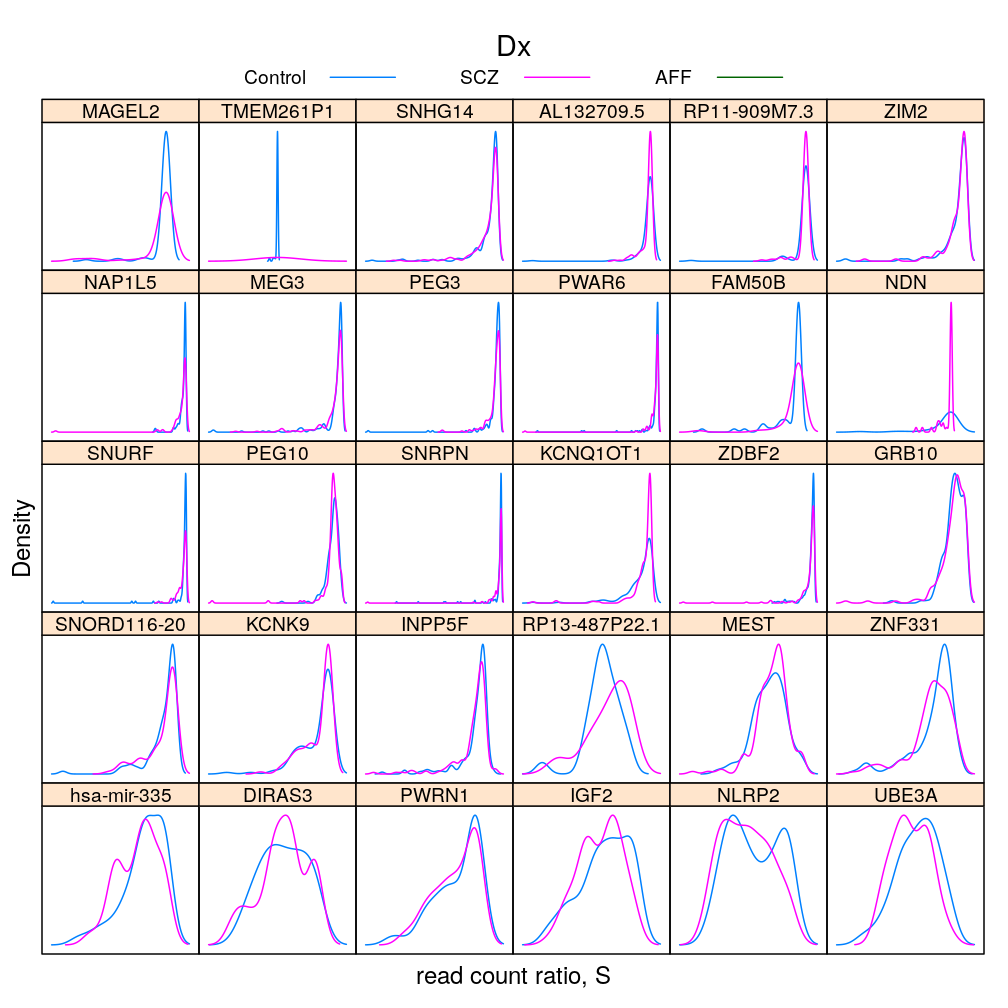
The same information (extended with AFF) in box and whisker representation:
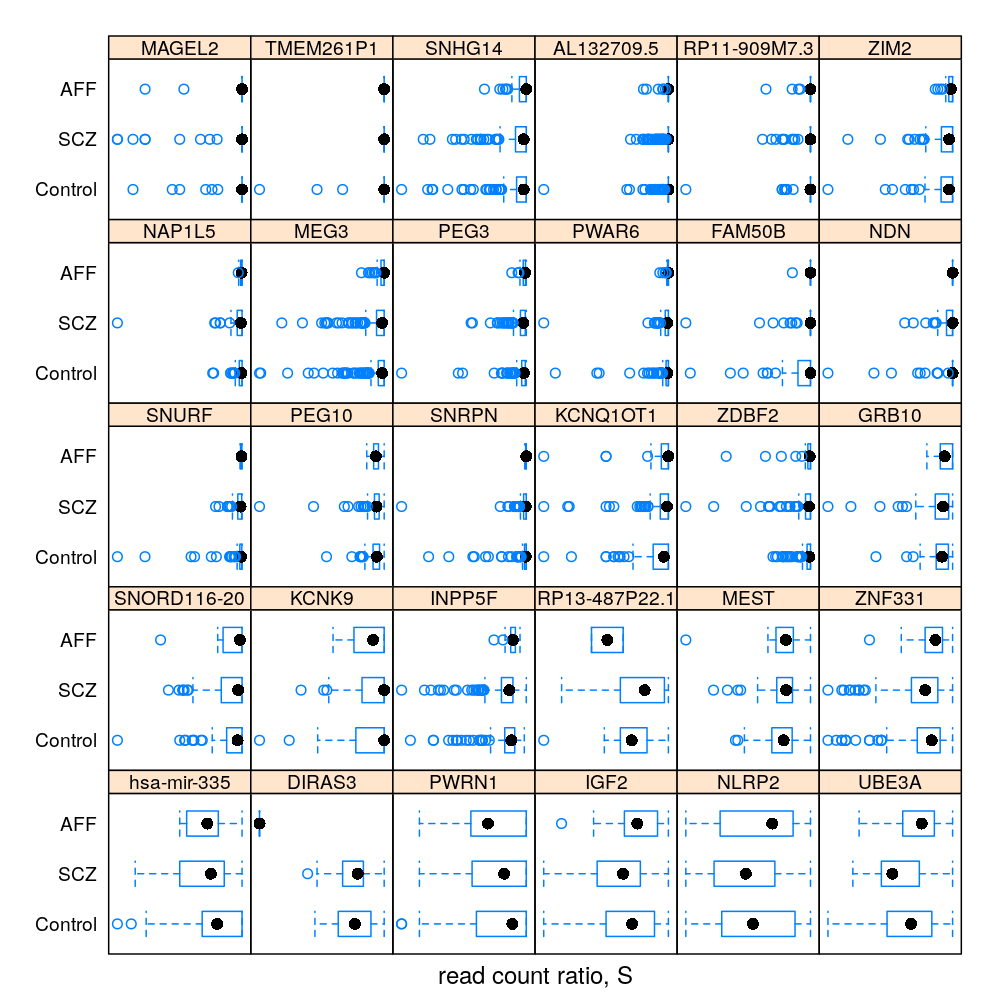
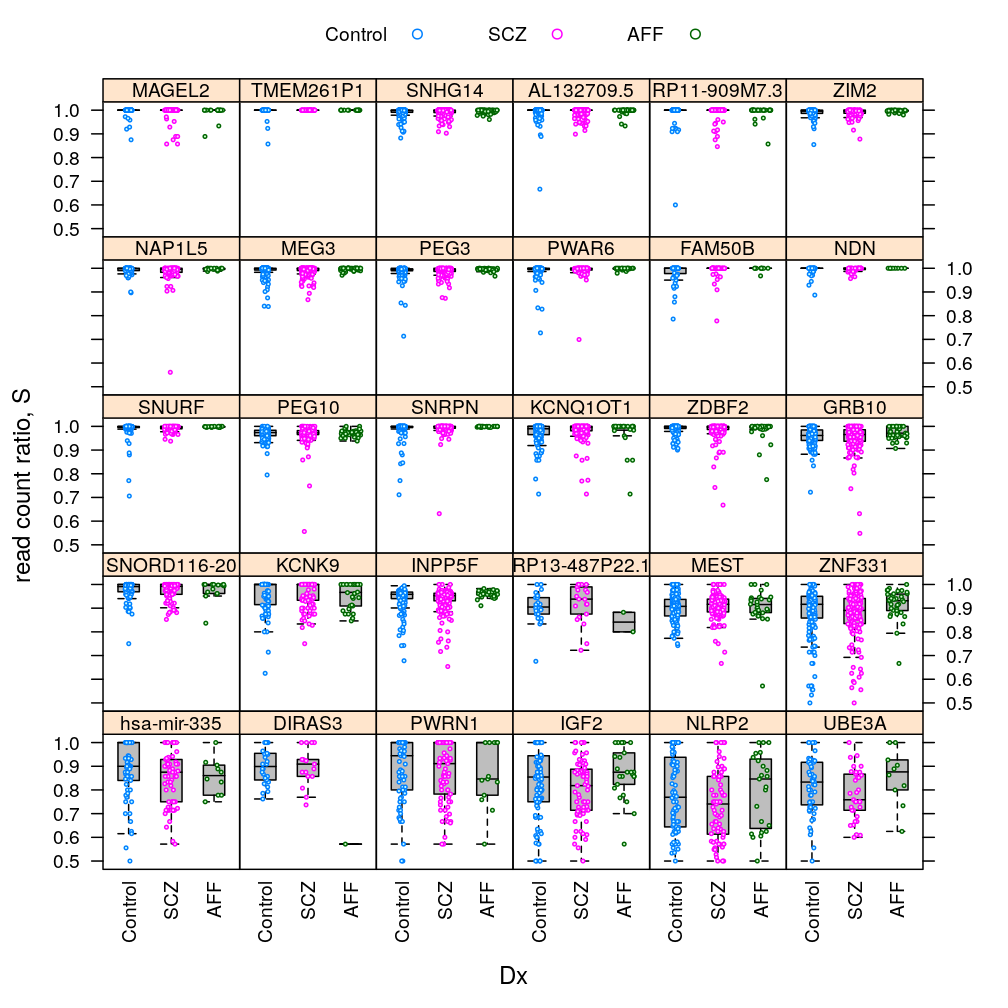
Q statistic
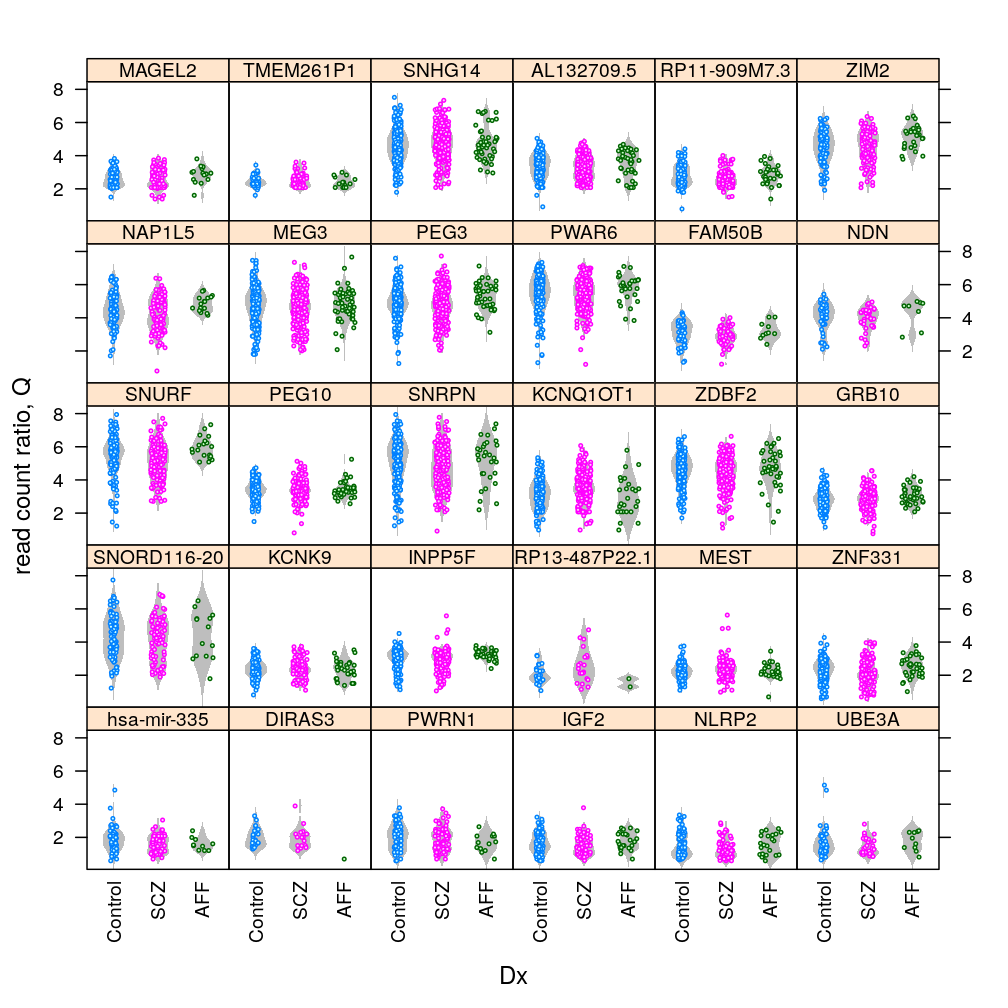
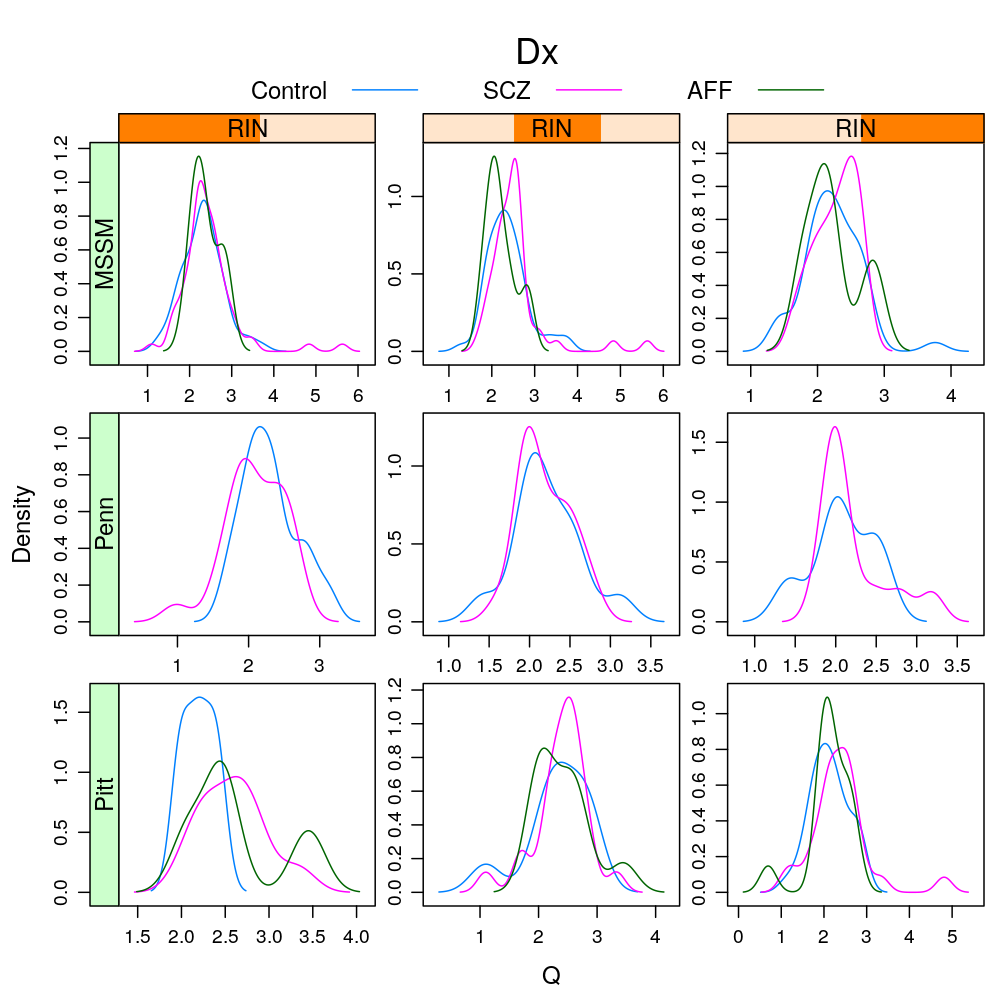
Only with MEST, the most significantly affected gene by Dx (see a later post), conditioning on various RIN intervals
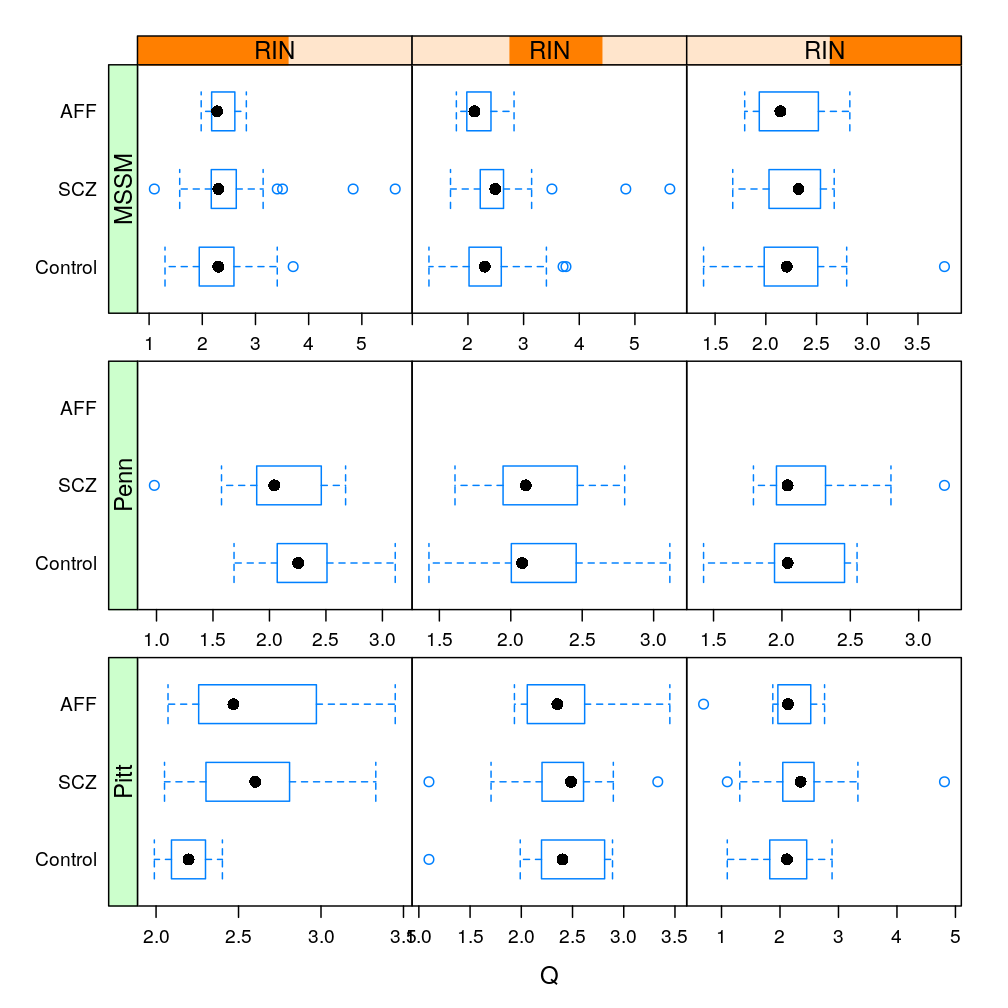
Correlation and gene proximity
gs <- read.csv("../../results/gene-clusters.csv", row.names = 1)[-1 * 2:14]
gs.sel <- gs[as.character(read.csv("../../data/genes.regression.new")[ , 1, drop = TRUE]), -1 * c(1, 6) ]
gs.sel$Gene <- factor(rownames(gs.sel), levels = rownames(gs.sel), ordered = TRUE)
gs.sel <- gs.sel[with(gs.sel, order(seg, start)), ]
gs.sel[c("cluster", "start", "gene.type")]
## cluster start gene.type
## DIRAS3 clus 2 (chr 1) 68511644 protein_coding
## ZDBF2 clus 4 (chr 2) 207139386 protein_coding
## NAP1L5 clus 5 (chr 4) 89617065 protein_coding
## FAM50B clus 7 (chr 6) 3849619 protein_coding
## GRB10 clus 11 (chr 7) 50657759 protein_coding
## PEG10 clus 13 (chr 7) 94285636 protein_coding
## MEST clus 14 (chr 7) 130126011 protein_coding
## hsa-mir-335 clus 14 (chr 7) 130135634 antisense
## KCNK9 clus 17 (chr 8) 140613080 protein_coding
## INPP5F clus 19 (chr 10) 121485608 protein_coding
## IGF2 clus 20 (chr 11) 2150341 protein_coding
## KCNQ1OT1 clus 20 (chr 11) 2629557 antisense
## MEG3 clus 27 (chr 14) 101245746 lincRNA
## AL132709.5 clus 27 (chr 14) 101403737 lincRNA
## RP11-909M7.3 clus 27 (chr 14) 101433988 lincRNA
## MAGEL2 clus 28 (chr 15) 23888690 protein_coding
## NDN clus 28 (chr 15) 23930564 protein_coding
## PWRN1 clus 28 (chr 15) 24738283 lincRNA
## SNRPN clus 28 (chr 15) 25068793 protein_coding
## SNURF clus 28 (chr 15) 25200132 protein_coding
## PWAR6 clus 28 (chr 15) 25277019 lincRNA
## SNORD116-20 clus 28 (chr 15) 25332807 lincRNA
## TMEM261P1 clus 28 (chr 15) 25414483 pseudogene
## SNHG14 clus 28 (chr 15) 25497371 snoRNA
## UBE3A clus 28 (chr 15) 25582380 protein_coding
## RP13-487P22.1 clus 28 (chr 15) 25590779 sense_intronic
## ZNF331 clus 32 (chr 19) 54024234 protein_coding
## NLRP2 clus 32 (chr 19) 55464497 protein_coding
## ZIM2 clus 32 (chr 19) 57285919 protein_coding
## PEG3 clus 32 (chr 19) 57321444 protein_coding
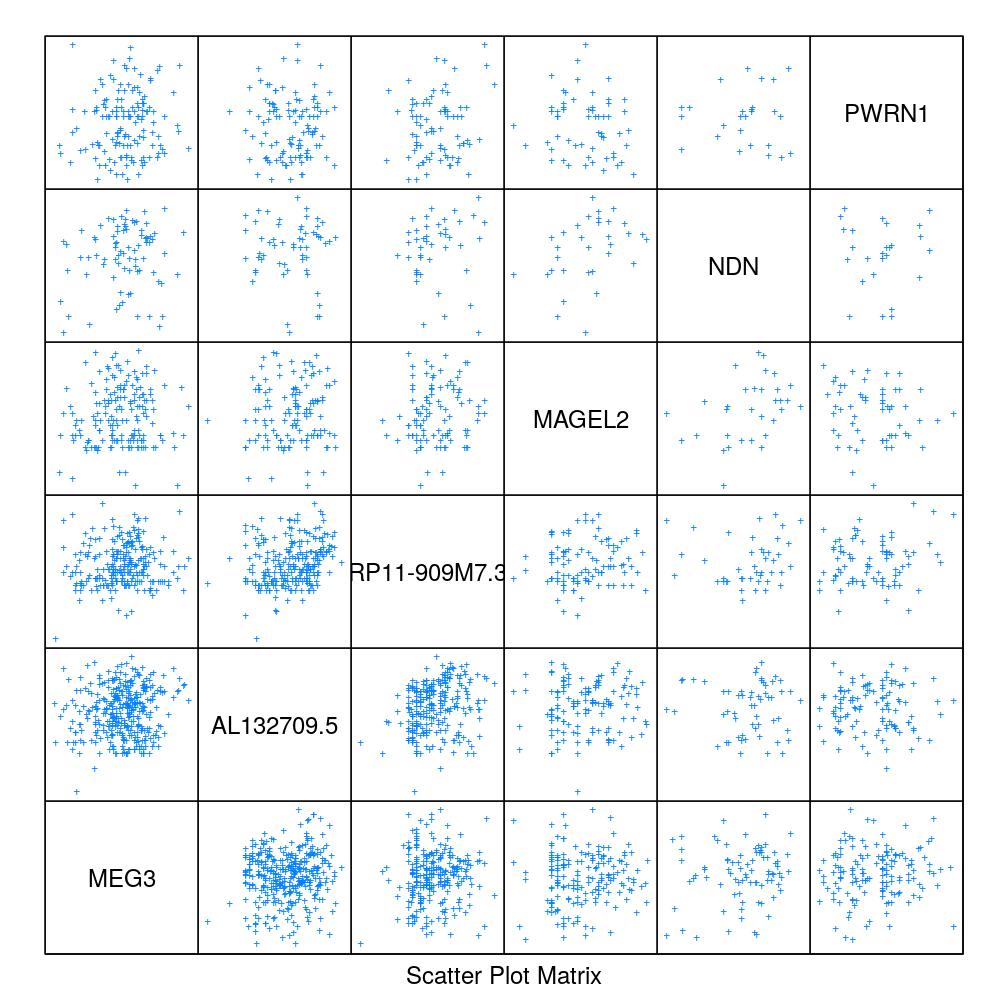
Select 3-3 consecutive genes in cluster 27 (chr 14) and 28 (chr 15), respectively. Produce scatter plot matrix as well as parallel plot first using the S statistic and then the Q statistic. These plots show no clear pattern in which correlation would depend on gene proximity.
S statistic
sel.g <- as.character(gs.sel[gs.sel$seg %in% c(27, 28), "Gene"])[1:6]
splom(m <- sapply(get.readcounts(gene.ids)[sel.g], getElement, "S"), pch = "+", pscales = 0)

parallelplot(m)
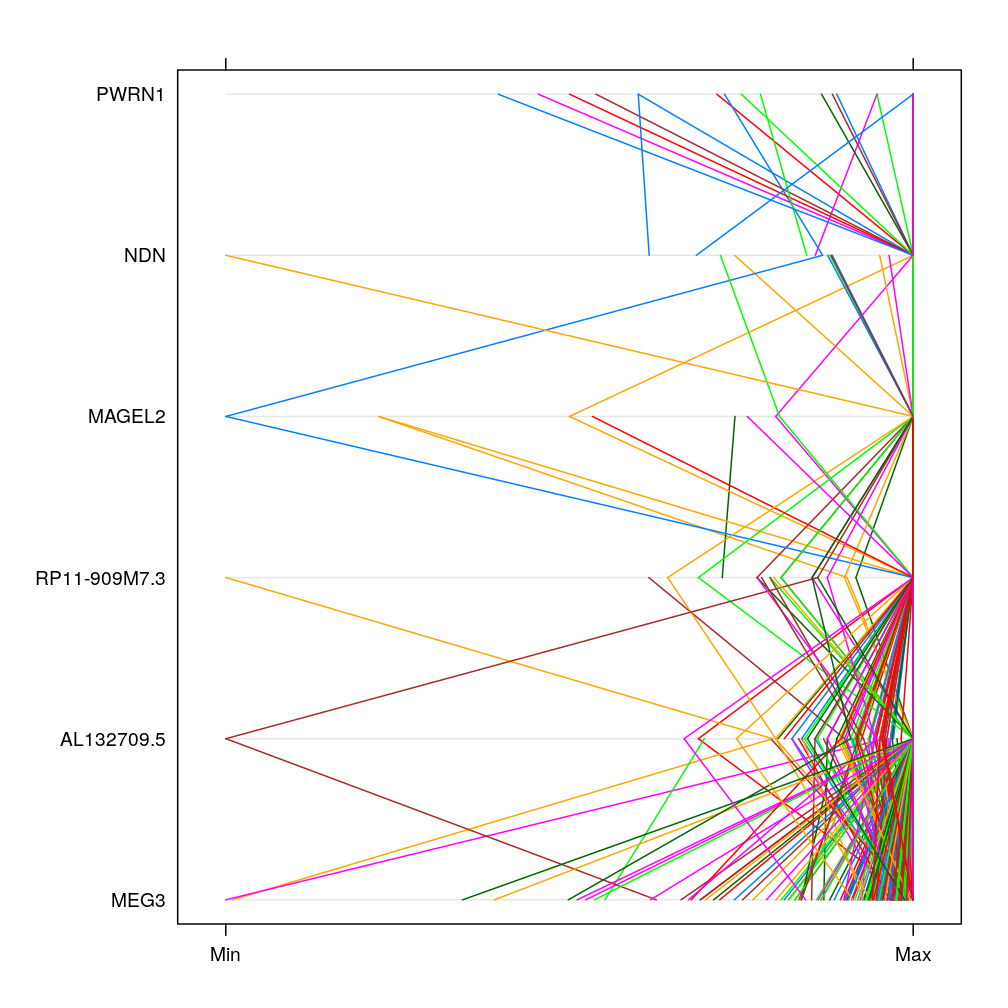
Q statistic
splom(m <- sapply(get.readcounts(gene.ids)[sel.g], getElement, "Q"), pch = "+", pscales = 0)
parallelplot(m)